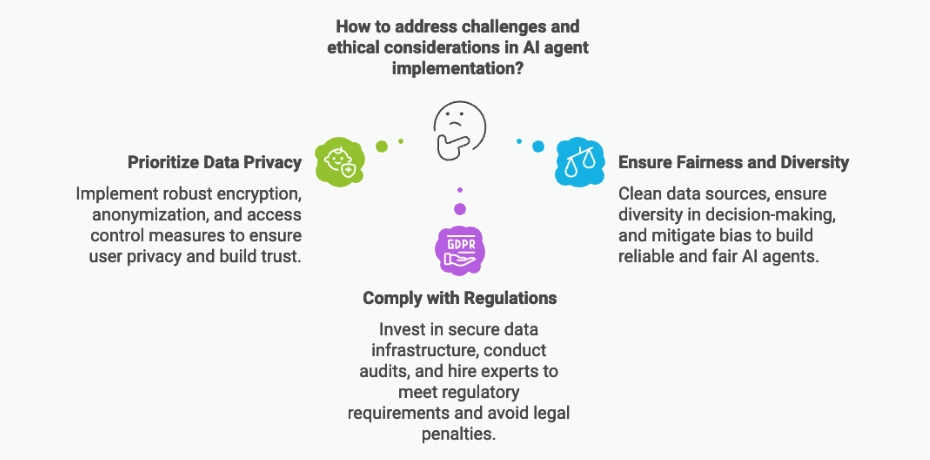
AI Agents: The Reliability Challenge
AI Agents: Reliability Over Capability
While AI agents are becoming increasingly practical, their reliability remains a significant challenge. Unlike traditional data processing systems that deliver predictable results, AI agents operate on stochastic algorithms, which introduce inherent randomness and uncertainty. This unpredictability makes it difficult to ensure consistent performance across different contexts.
Key Challenges in AI Agent Reliability
- Stochastic Nature: AI agents often produce varying results based on context, making it hard to achieve repeatable outcomes. For example, the same algorithm might yield different results in different scenarios.
- Shared Memory: Current AI models lack persistent, shared memory, which means they treat each situation as entirely new, even if it has occurred before. This inefficiency can lead to redundant problem-solving processes.
- Complex Interactions: Coordinating multiple AI agents, each operating on stochastic algorithms, adds layers of complexity. Ensuring reliable interactions among these agents is a major engineering feat.
Potential Solutions
Researchers are exploring ways to enhance AI agent reliability by extending the context length or maximum short-term memory of models. Projects like MemGPT aim to build memory managers for large language models, which could allow agents to learn from past actions and make more predictable decisions.
Practical Applications
While AI agents may not yet be reliable enough for highly personalized tasks like scheduling meetings, they are better suited for well-defined processes that benefit from improved coordination. Over the next five to ten years, significant engineering efforts will focus on solving these reliability issues, making AI agents more practical for a broader range of applications.
Conclusion
As AI technology advances, the focus on reliability over raw capability will be crucial. Ensuring that AI agents can interact predictably and efficiently will unlock their full potential in various industries, from healthcare to business automation.