Converting Natural Language to SQL: Tools and Best Practices
April 05, 2025
Natural Language to SQL
AI
SQL Translator
OpenAI
Fine-Tuning
RAG
Schema Awareness
Database Interaction
This article explores the challenges, tools, and best practices for converting natural language to SQL queries using AI-powered solutions.
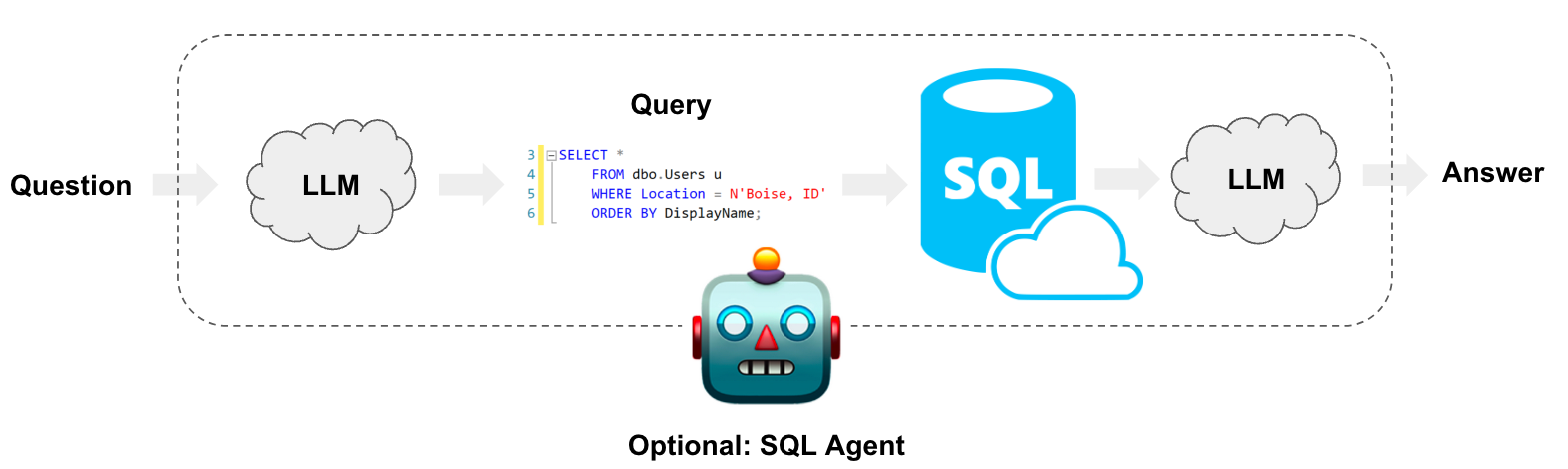
Converting Natural Language to SQL
Converting natural language to SQL queries is a powerful capability that leverages artificial intelligence to simplify database interactions. Here are some key insights and tools to help you achieve this:
Common Challenges
- Ambiguity in Natural Language: Phrases like "How many customers have logged in in the last 30 days?" can be interpreted in multiple ways (e.g., counting logins vs. unique customers).
- Schema Awareness: Providing detailed descriptions of database fields (e.g., "lastLogin" as "last login activity date") helps the model generate accurate queries.
- Consistency Across Queries: Ensuring the same SQL query is generated for semantically similar questions (e.g., "active customers" vs. "logged-in customers") can be tricky.
Tools and Approaches
- SQL Translator: A free and open-source tool (GitHub) that converts natural language to SQL and vice versa. It supports features like dark mode, schema awareness, and query history.
- OpenAI API: Platforms like OpenAI provide examples for translating natural language to SQL (OpenAI Example). Fine-tuning models or using prompt engineering can improve accuracy.
- Fine-Tuning and RAG: For complex use cases, fine-tuning models (e.g., using LoRA or QLoRA) and leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can enhance SQL generation for specific schemas and datasets.
Best Practices
- Provide clear context, including table layouts and field descriptions, to guide the model.
- Use embeddings to handle semantic similarities between questions, but ensure the model architecture supports this approach.
- Experiment with temperature settings (e.g., temperature 0) to generate consistent and accurate queries.
Example
Natural Language: "How many customers have logged in in the last 30 days?"
SQL Query: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) FROM logins WHERE last_login >= NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days';
For more details, explore the SQL Translator or check out the OpenAI Community Discussion.
Sources
Transforming Natural Language Text to SQL - Levio Consulting
The main idea is to create patterns and matches, both full and partial, and feed them into SQL schema-based rules to transform the natural text ...
Converting natural language to SQL query - API
I am trying to convert the natural language into SQL queries. Could you please provide some common problems in the conversion?
SQL Translator is a tool for converting natural language ... - GitHub
SQL Translator is a tool for converting natural language queries into SQL code using artificial intelligence. This project is 100% free and open source.