SpatialVLA
by Shanghai AI Lab, China Telecom AI Research Institute, ShanghaiTechWhat is SpatialVLA?
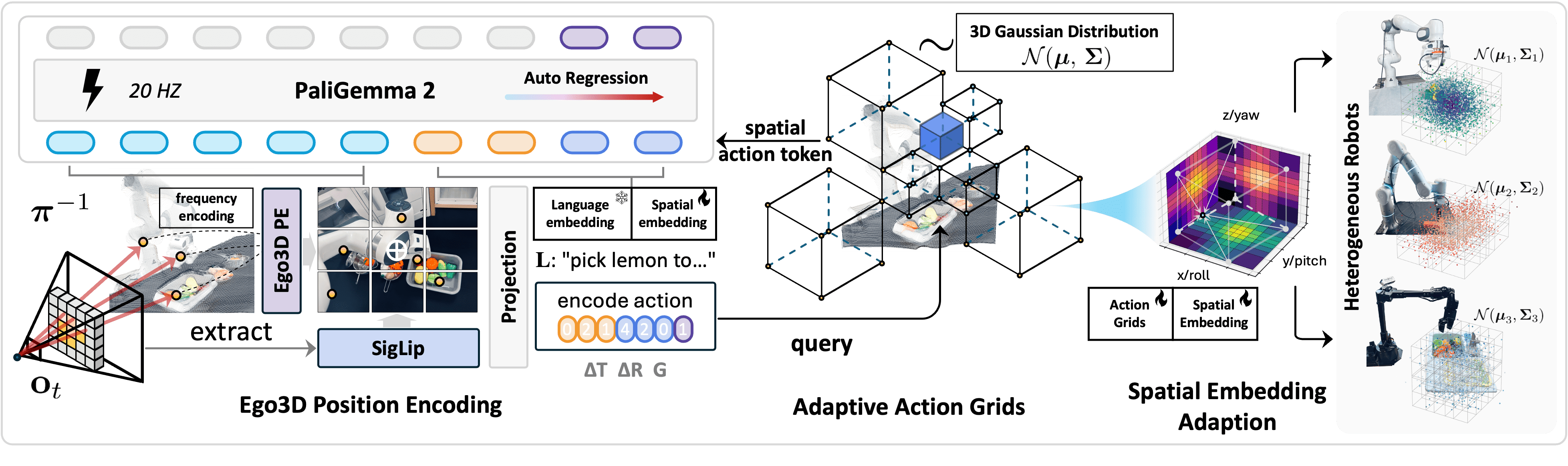
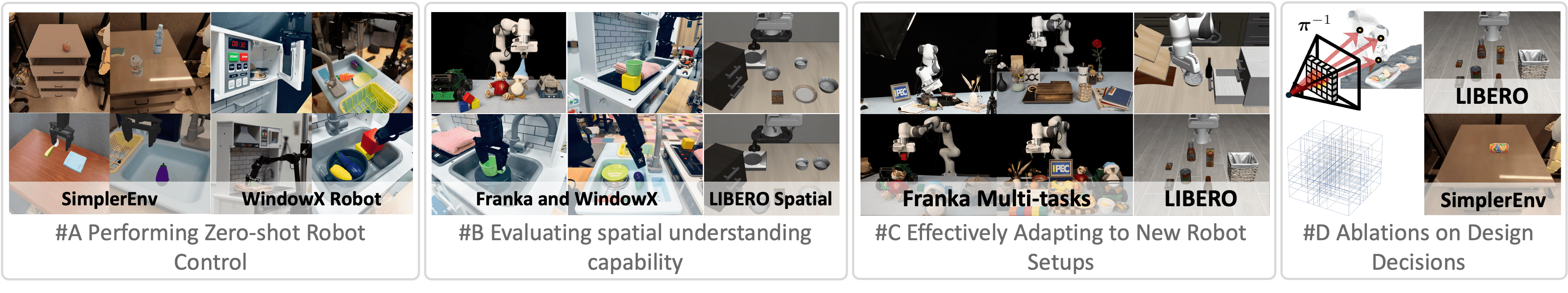
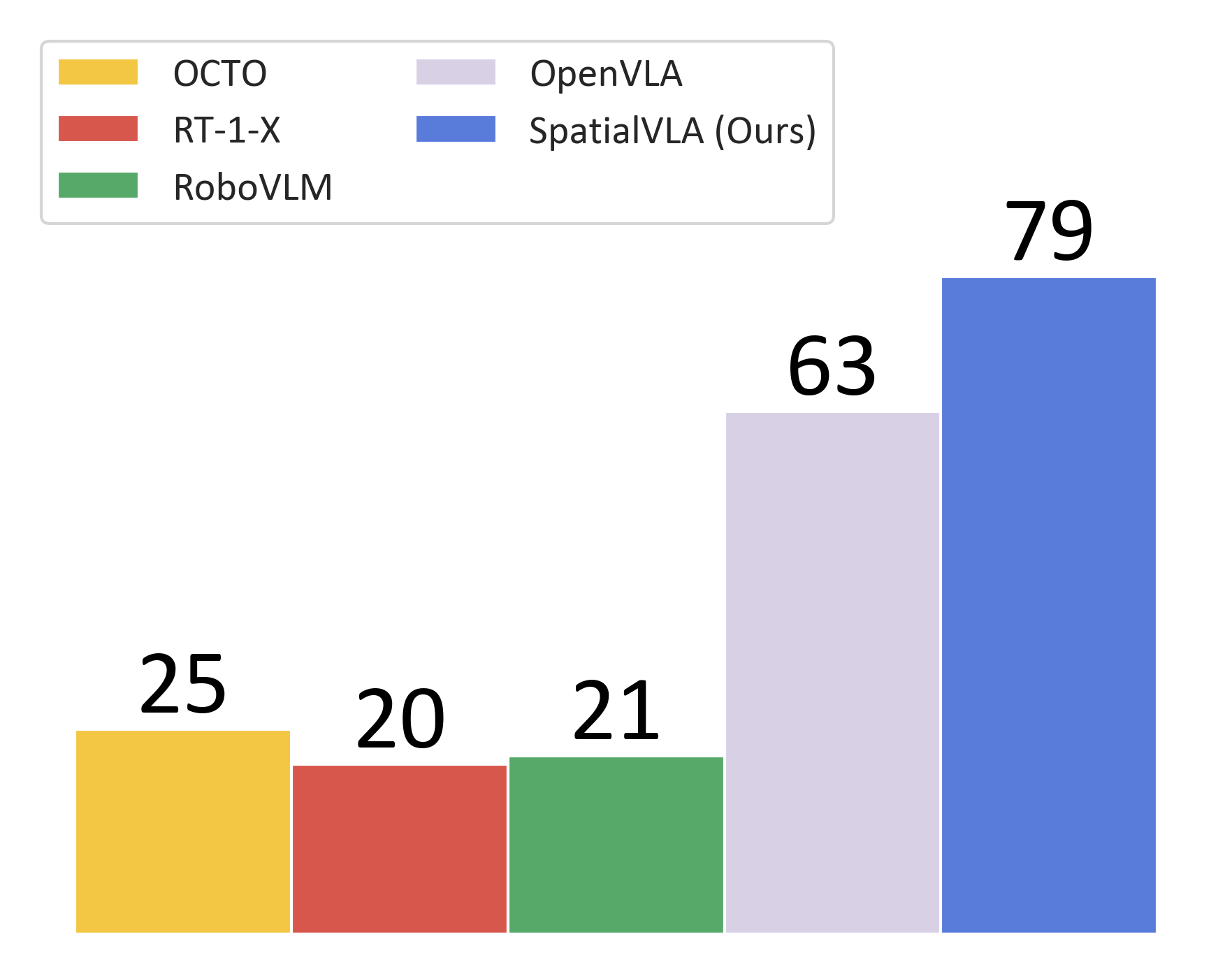
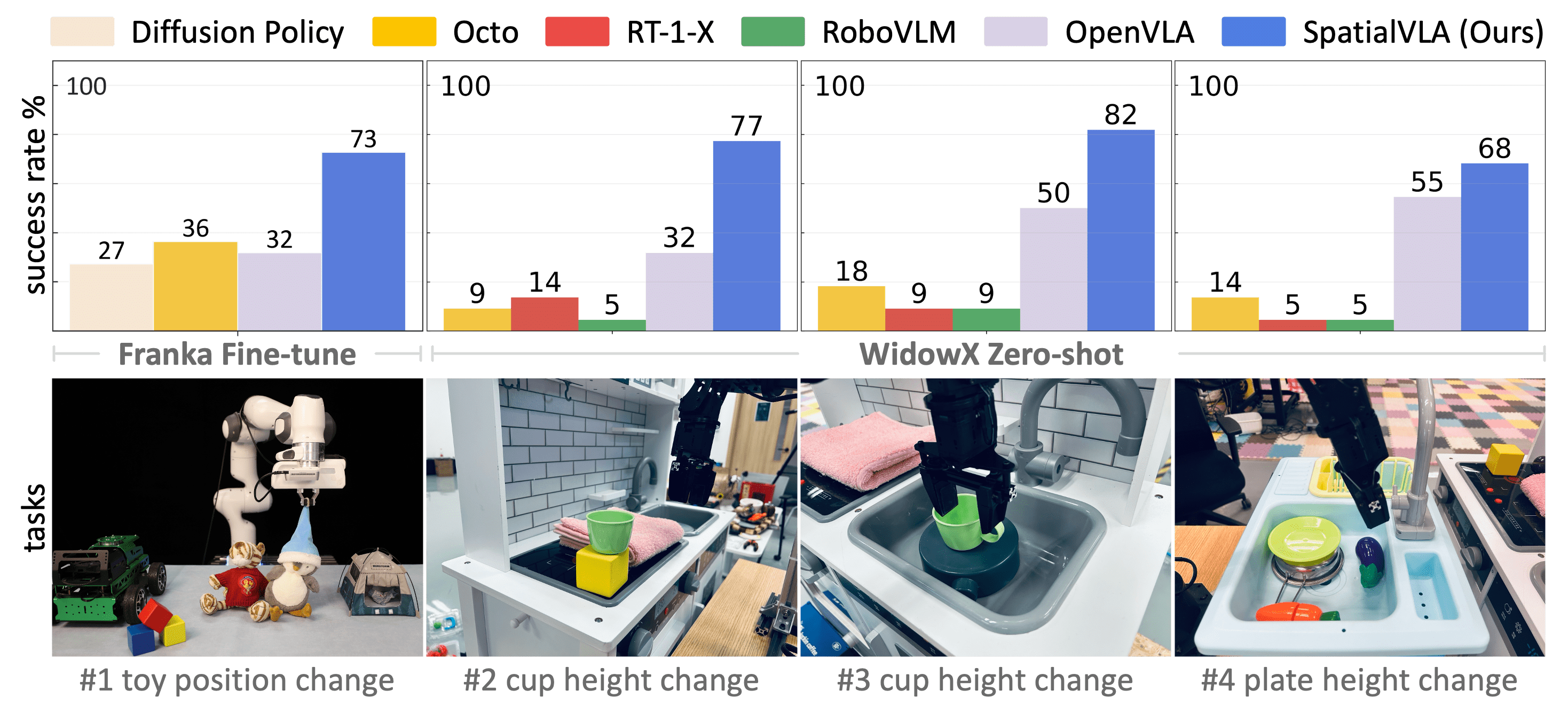
SpatialVLA is a novel spatial embodied general operation model jointly developed by Shanghai AI Lab, China Telecom AI Research Institute, and ShanghaiTech. It is pre-trained on millions of real-world data points to endow robots with universal 3D spatial understanding capabilities. By integrating 3D spatial information with semantic features using Ego3D position encoding and discretizing continuous actions with adaptive action grids, SpatialVLA achieves cross-platform generalization control for robots. It demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization and spatial understanding abilities, excelling in complex environments and multi-task scenarios. The open-source code and flexible fine-tuning mechanisms provide new technical pathways for robotics research and applications.
Main Features of SpatialVLA
- Zero-shot Generalization Control: Execute operations in unseen robot tasks and environments directly without additional training.
- Efficient Adaptation to New Scenarios: Quickly adapt to new robot platforms or tasks with minimal data fine-tuning.
- Strong Spatial Understanding: Understand complex 3D spatial layouts and perform precise operations such as object localization, grasping, and placement.
- Cross-platform Universality: Supports various robot forms and configurations, enabling universal operation strategies.
- Fast Inference and Efficient Action Generation: Based on discretized action spaces, it improves model inference speed, making it suitable for real-time robot control.
Technical Principles of SpatialVLA
- Ego3D Position Encoding: Combines depth information with 2D semantic features to build a robot-centric 3D coordinate system, eliminating the need for specific robot-camera calibration and allowing the model to perceive 3D scene structures adaptable to different robot platforms.
- Adaptive Action Grid: Discretizes continuous robot actions into adaptive grids, dividing the action space based on data distribution. Actions of different robots are aligned with the grid, enabling cross-platform action generalization and transfer.
- Spatial Embedding Adaptation: During the fine-tuning phase, the grid is re-divided based on the new robot's action distribution, adjusting spatial embeddings. This provides a flexible and efficient robot-specific post-training method, accelerating model adaptation to new environments.
- Pre-training and Fine-tuning: Pre-trained on large-scale real robot data to learn general operation strategies, and fine-tuned on new tasks or robot platforms to further optimize model performance.
Project Links
- Project Website: https://spatialvla.github.io/
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/SpatialVLA/SpatialVLA
- HuggingFace Model Library: https://huggingface.co/IPEC-COMMUNITY/foundation-vision-language-action-model
- arXiv Technical Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.15830
Application Scenarios
- Industrial Manufacturing: Used for automated assembly and part handling, quickly adapting to different production lines to improve efficiency.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Precisely grasp and transport goods, adapt to dynamic environments, and optimize logistics efficiency.
- Service Industry: Perform delivery, cleaning, and organization tasks, understand natural language instructions, and adapt to complex environments.
- Medical Assistance: Pass surgical instruments, transport medicines, and ensure precise and safe operations.
- Education and Research: Support rapid development and testing of new robot applications, aiding academic research.
Model Capabilities
Usage & Integration
Screenshots & Images