Trending Models Most popular AI models and foundation models
GPT-4 is OpenAI's most advanced large language model, demonstrating human-level performance on various academic and professional tests.
Meta's open-source large language model family, offering strong performance across various tasks with different model sizes.
An open-source text-to-image model capable of generating detailed images from text descriptions, with a strong community and multiple deployment options.
Anthropic's most capable AI model, featuring enhanced reasoning, analysis, and creative capabilities with improved accuracy and safety.
Google's advanced language model optimized for reasoning, coding, and multilingual tasks with strong capabilities across various domains.
Google's most capable and flexible AI model, designed to be multimodal from the ground up with superior reasoning capabilities.
OpenAI's advanced text-to-image generation model capable of creating highly detailed and accurate images from natural language descriptions.
A family of powerful open-source language models known for their efficiency and strong performance across various tasks.
OpenAI's advanced speech recognition system capable of transcribing and translating multiple languages with high accuracy.
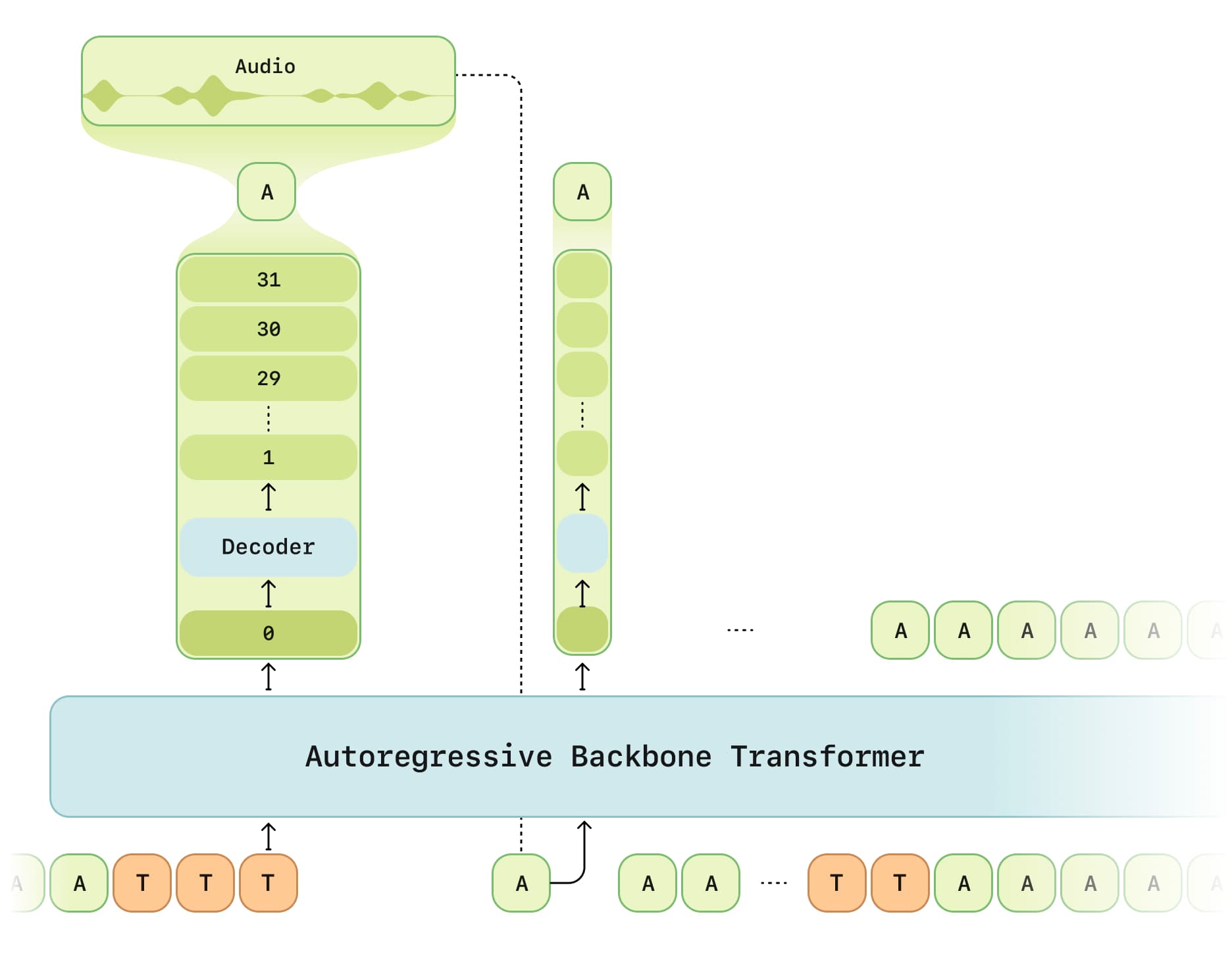
Ola is a full-modal language model developed by Tsinghua University, Tencent Hunyuan Research Team, and NUS S-Lab. It employs a progressive modal alignment strategy to gradually expand the modalities supported by the language model, starting with images and text, and then introducing audio and video data. Ola's architecture supports full-modal inputs, including text, images, video, and audio, and can process these inputs simultaneously. It also features a sentence-by-sentence decoding scheme for streaming speech generation, enhancing interactive experiences.
All Models Complete list of AI models and foundation models, sorted by newest first
Ola is a full-modal language model developed by Tsinghua University, Tencent Hunyuan Research Team, and NUS S-Lab. It employs a progressive modal alignment strategy to gradually expand the modalities supported by the language model, starting with images and text, and then introducing audio and video data. Ola's architecture supports full-modal inputs, including text, images, video, and audio, and can process these inputs simultaneously. It also features a sentence-by-sentence decoding scheme for streaming speech generation, enhancing interactive experiences.
Zonos is a high-fidelity text-to-speech (TTS) model developed by Zyphra. It includes two models: a 1.6 billion parameter Transformer model and an SSM hybrid model, both open-sourced under the Apache 2.0 license. Zonos generates natural and expressive speech based on text prompts and speaker embeddings, supporting voice cloning and adjustable parameters such as speed, pitch, and emotion. The output sampling rate is 44kHz. The model is trained on approximately 200,000 hours of multilingual speech data, primarily supporting English with limited support for other languages. Zonos provides an optimized inference engine for fast speech generation, making it suitable for real-time applications.
Step-Video-T2V is an open-source text-to-video model developed by Leapfrogging Star, featuring 30 billion parameters and capable of generating high-quality videos up to 204 frames long. The model uses a deeply compressed variational autoencoder (Video-VAE) for efficient training and inference, supporting bilingual text inputs in Chinese and English. It employs a diffusion-based Transformer (DiT) architecture with a 3D full-attention mechanism, optimized for generating videos with strong motion dynamics and high aesthetic quality.
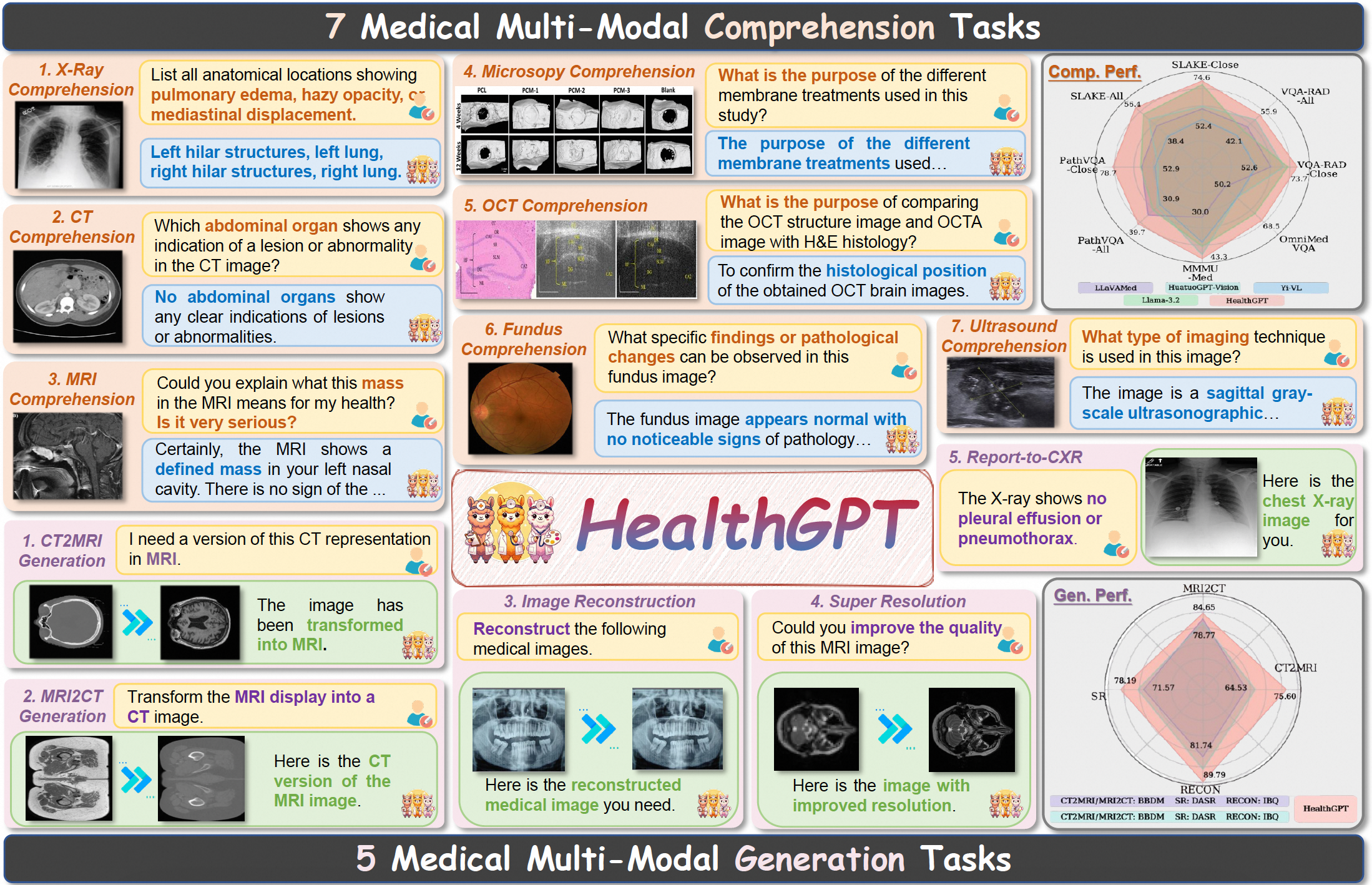
HealthGPT is an advanced medical visual language model (Med-LVLM) developed by Zhejiang University, University of Electronic Science and Technology, and Alibaba. It integrates visual comprehension and generation tasks using Heterogeneous Low-Rank Adaptation (H-LoRA) technology, enabling efficient medical image analysis, diagnostic assistance, and text generation. The model offers two versions: HealthGPT-M3 (3.8 billion parameters) and HealthGPT-L14 (14 billion parameters), optimized for different performance and resource needs. HealthGPT employs Hierarchical Visual Perception (HVP) and a Three-Stage Learning Strategy (TLS) to enhance visual feature learning and task adaptation.
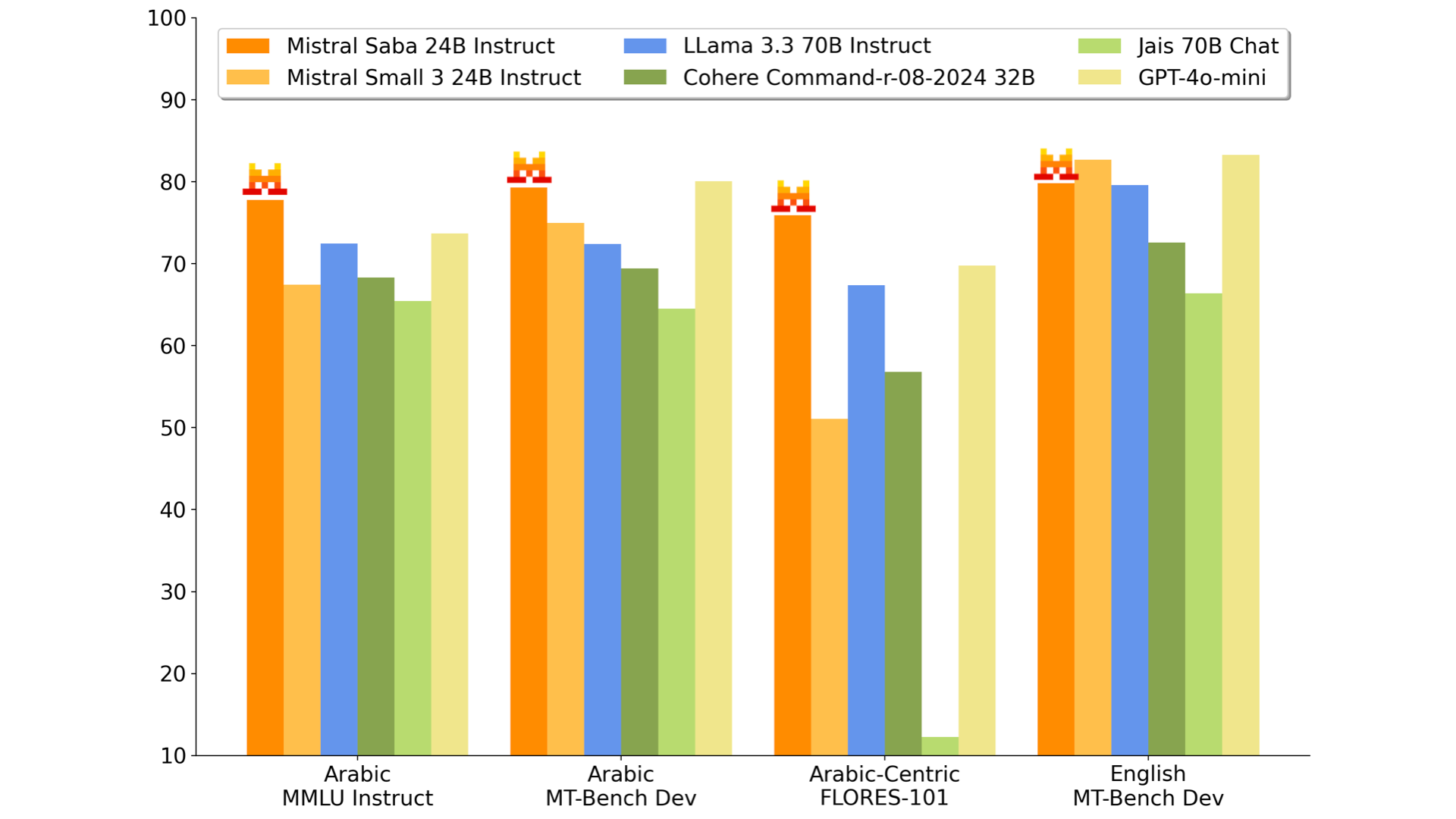
Mistral Saba is a 24-billion-parameter AI model developed by Mistral AI, specifically designed to handle Middle Eastern and South Asian languages and cultures. It excels in processing Arabic and Indian-origin languages such as Tamil and Malayalam, offering efficient deployment on single GPU systems with a response speed of 150 tokens per second. The model addresses the limitations of general-purpose models in understanding regional language nuances and cultural contexts.
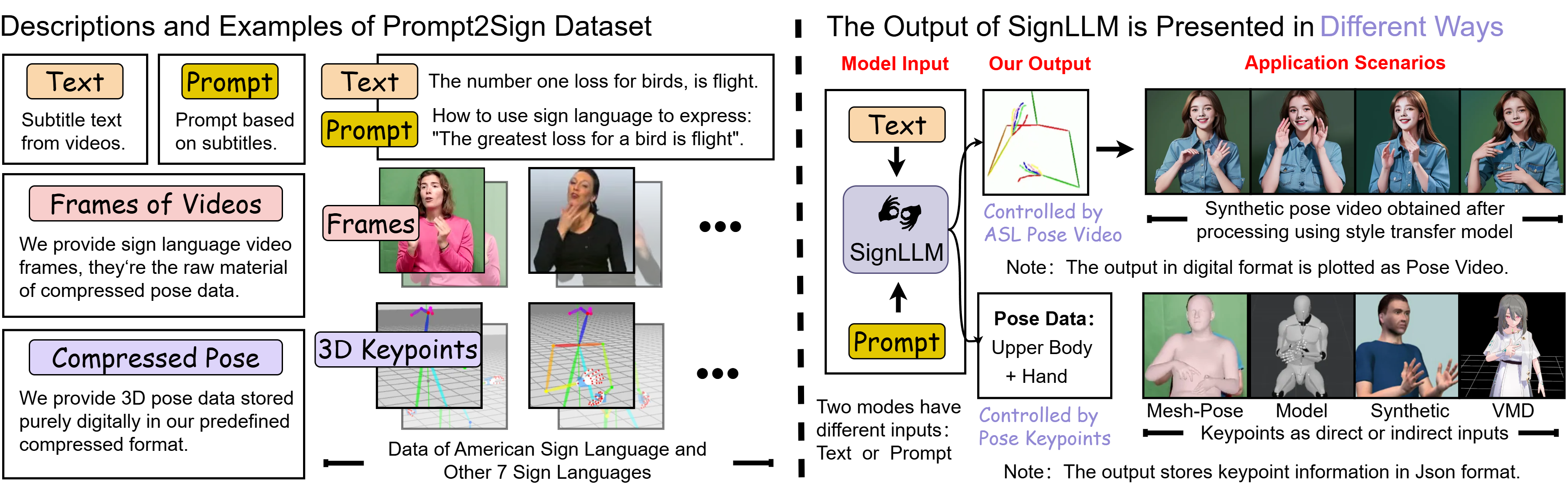
SignLLM is a groundbreaking multilingual sign language generation model that transforms text input into corresponding sign language videos. It supports multiple sign languages, including American Sign Language (ASL), German Sign Language (GSL), Argentine Sign Language (LSA), and Korean Sign Language (KSL). The model leverages the Prompt2Sign dataset, utilizing automated techniques to collect and process sign language videos from the web. It incorporates new loss functions and reinforcement learning modules to achieve efficient data extraction and model training.
Flame is an open-source multimodal AI model that transforms UI design screenshots into high-quality modern frontend code. It leverages visual language modeling, automated data synthesis, and structured training processes to generate code that adheres to modern frontend frameworks like React. Flame supports componentization, state management, and dynamic interactions, overcoming the limitations of traditional models that generate static code. The model's training data, models, and test sets are open-source, providing an efficient design-to-code conversion tool for frontend development.
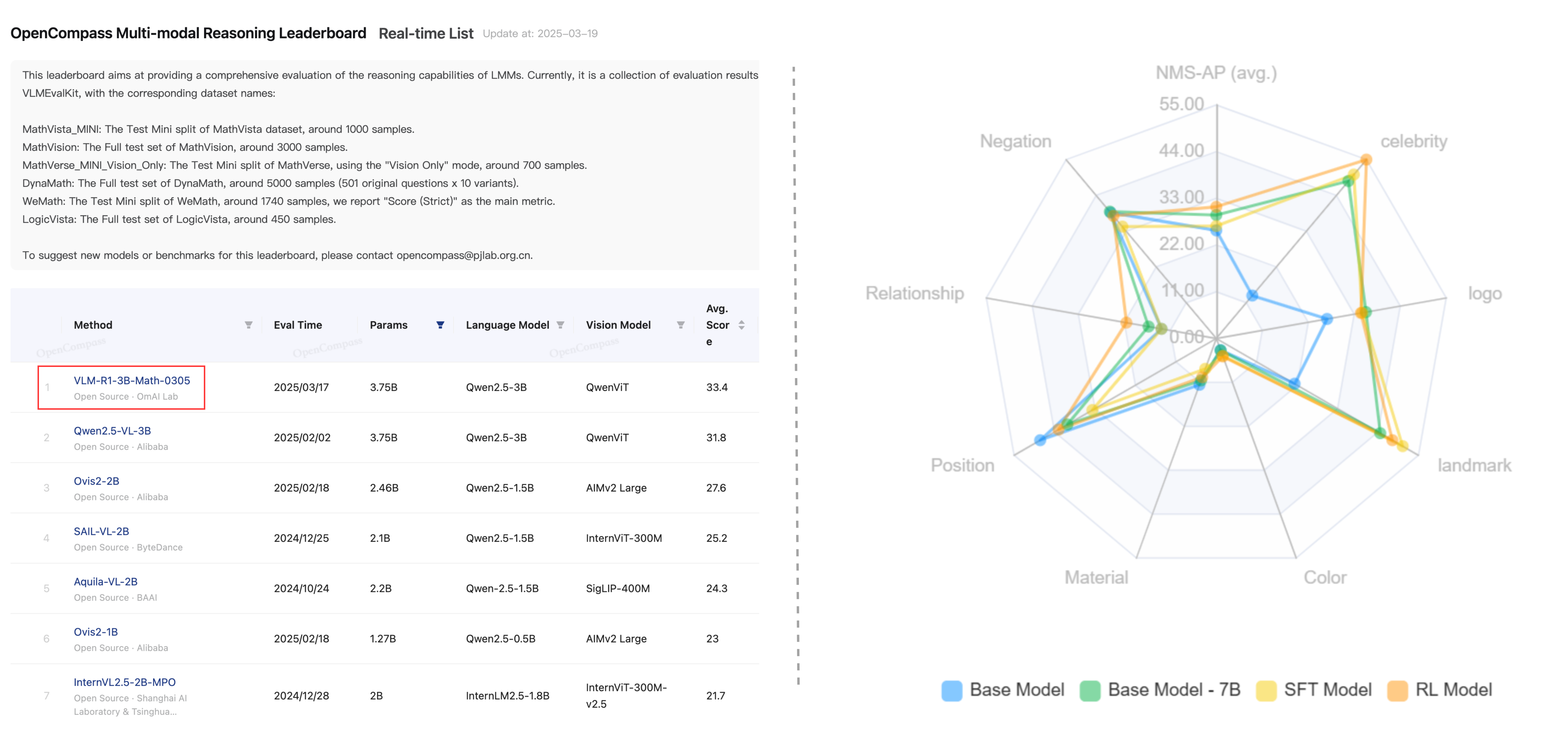
VLM-R1, developed by Om AI Lab, is a cutting-edge visual language model that leverages reinforcement learning to accurately identify and locate target objects in images using natural language instructions. Built on the Qwen2.5-VL architecture and enhanced with DeepSeek's R1 method, VLM-R1 excels in complex scenes and cross-domain data, offering superior generalization and stability. It supports multimodal reasoning, joint image-text processing, and efficient training, making it a powerful tool for applications ranging from smart assistants to medical imaging analysis.
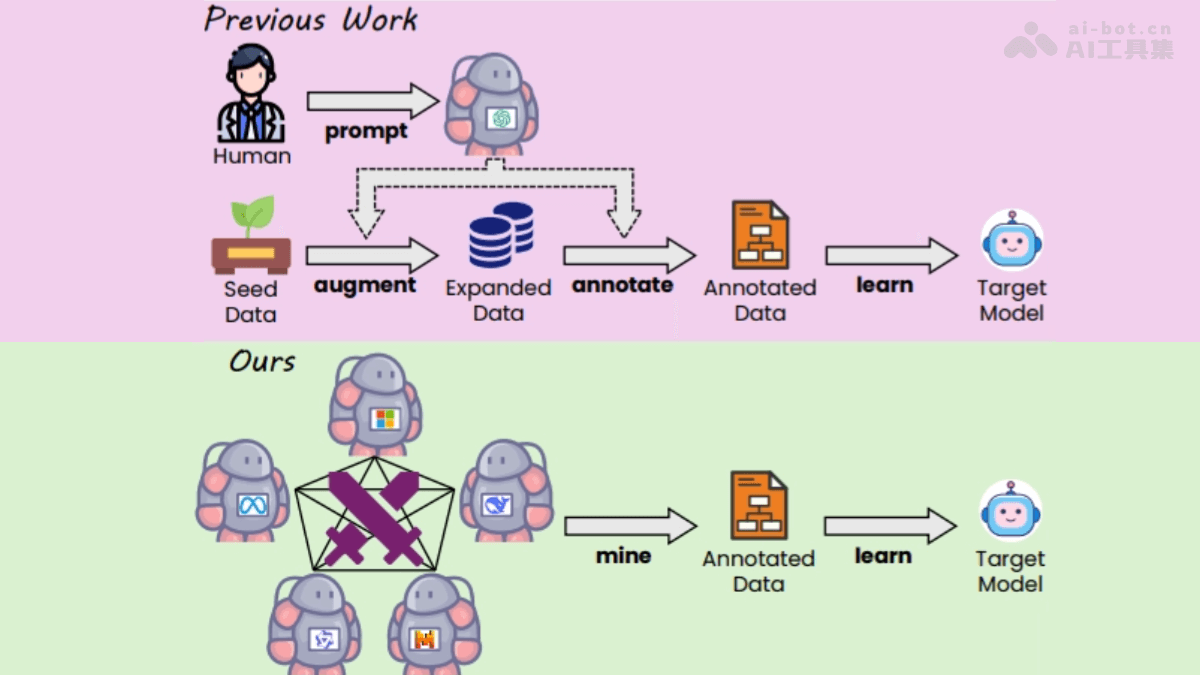
WarriorCoder is a code generation large language model (LLM) developed by the School of Computer Science and Engineering at South China University of Technology in collaboration with Microsoft. It generates high-quality training data through adversarial simulations between expert models, enhancing model performance. Unlike traditional methods, WarriorCoder does not rely on existing proprietary models or datasets. Instead, it mines instructions from scratch, using the Elo rating system and a referee model to evaluate adversarial outcomes and select the best responses as training data. WarriorCoder integrates the strengths of multiple open-source code expert models, avoiding human intervention and system bias during data collection. Experiments show that WarriorCoder achieves new SOTA performance in tasks such as code generation, code reasoning, and library usage, demonstrating strong generalization capabilities and data diversity.
CSM (Conversational Speech Model) is a voice dialogue model developed by the Sesame Team, designed to improve the naturalness and emotional interaction capabilities of voice assistants. It uses a multimodal learning framework, combining text and voice data, and leverages the Transformer architecture to generate natural and coherent speech. CSM dynamically adjusts tone, rhythm, and emotional expression based on conversation history and context, providing a more human-like interaction experience. It is optimized for training efficiency and trained on large-scale datasets to enhance performance and expressiveness.